-
About Us
button

Dabur India Limited is a leading Indian consumer goods company with interests in Hair Care, Oral Care, Health Care, Skin Care, Home Care and Food & Beverages.
-
Our Brands
button

Dabur presents a range of Herbal & Ayurvedic Personal Care products, created to make you look and feel good. Bringing together the gentle touch of nature and Ayurveda's wisdom .
-
Investors
button

Read our recent and archived releases, quarterly results, annual reports and financial statements. Initiatives Investor Centre.
-
Newsroom
button

Welcome to Dabur Media Centre. In this section, you’ll find our latest Press Releases arranged in a chronological order. The Press Releases have been further
-
Ayurveda & you
button

Our curated Collection of Ayurvedic knowledge for you. We at Dabur are working towards helping people lead a healthy and balanced life.
-
Sustainability
button
Dabur has been engaged in community development activities since 1994 and is committed to making a positive contribution to the communities where we source, live, work and sell our products.
-
Join Us
button

At Dabur, we are very passionate about winning and this has been engrained in DNA of the organization.
-
Support
button
- Home > Ayurveda & you > Ayurveda & Science > Ayurvedic & Medicinal Plants
Ayurveda and Science
Neem/नीम/Nimba/Margosa Tree/Azadirachta Indica
AYURVEDIC & MEDICINAL PLANTS

Uses Of Neem / Azadirachta Indica
Neem is considered a boon for mankind by nature. Use of Neem has been recommended by Ayurveda for a wide range of diseases. Such usage are attributed to its purification effect on blood. Scientific research on Neem demonstrates it to be a Panacea. It is suggested to be an antibacterial, anthelmintic, antiviral, anticancer and more importantly Immunomodulatory agent.
There are numerous benefits and uses of neem leaves as follows:
- Treats Acne
Neem has an anti-inflammatory property which helps reduces acne. Azadirachta Indica also helps reduce skin blemishes.
- Nourishes Skin
Neem is a rich source of Vitamin E which help repair damaged skin cells.
- Treats Fungal Infections
Neem has scientifically proven antifungal property which helps treat fungal infections.
- Useful in Detoxification
Neem can prove useful in detoxification both internally and externally. Consumption of neem leaves or powder stimulates kidneys and liver increasing the metabolism and eliminating the toxins out of the body. Externally, neem scrubs or paste can be used to remove germs, bacteria, dirt, etc from your skin preventing rashes and skin diseases.
- Increases Immunity
Neem is known for its antimicrobial and antibacterial effects. These properties play a huge role in boosting immunity.
- Insect & Mosquito Repellent
You can burn a few neem leaves to ward off the insects. This is also effective against different types of mosquitoes . From all the home remedies for malaria , neem is the best for treating the early symptoms of malaria.
- Prevents Gastrointestinal Diseases
Neem's anti-inflammatory properties help reduce inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract which helps reduce a series of diseases like constipation, stomach ulcer, flatulence, etc.
- Treats Wounds
Neem leaves have an antiseptic property which is why it is used to heal wounds.
- Reduces Dandruff
Neem is extensively used in shampoos and conditioners. Azadirachta Indica has antifungal and antibacterial properties which help eliminate dandruff and strengths your hair.
- Reduces Joint Pain
Application of neem oil or extract on the affected area can help reduce pain and discomfort. Hence it is widely used for treating arthritis.
- Exfoliates skin
Neem is an excellent exfoliant. It helps remove dead cells from the surface of the skin which will help prevent the growth of blemishes.
Chemical Composition
Neem plant contains flavonoids kemferol, quercetin and myricetin. The trunk bark contains nimbin, nimbinin, nimbosterol, tannins and a bitter principle margosine.
Balances kapha and pitta.
Read more about various ailments, it's causes, symptoms, ayurvedic treatments, etc.
Know the story behind other medicinal Ayurvedic ingredients
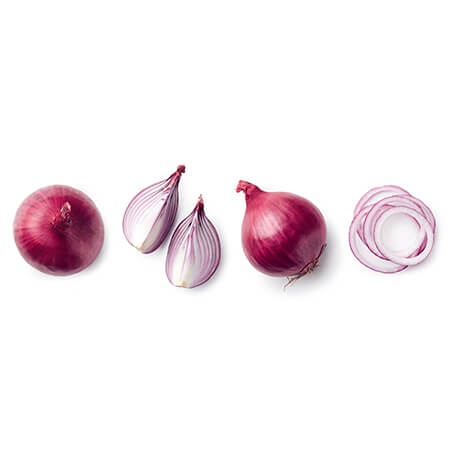

Onion
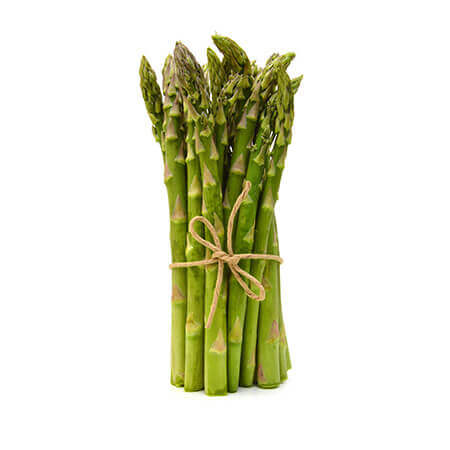

Shatavari
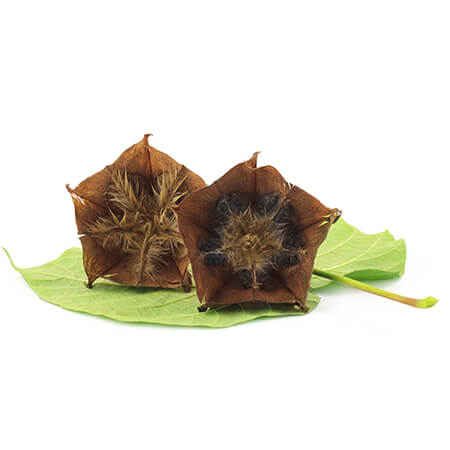

Ulatkambal
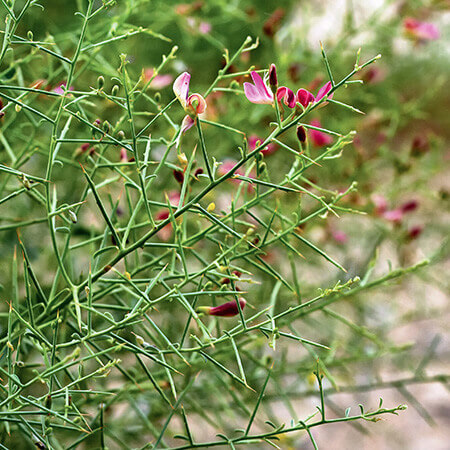

Yavasa





