-
About Us
button

Dabur India Limited is a leading Indian consumer goods company with interests in Hair Care, Oral Care, Health Care, Skin Care, Home Care and Food & Beverages.
-
Our Brands
button

Dabur presents a range of Herbal & Ayurvedic Personal Care products, created to make you look and feel good. Bringing together the gentle touch of nature and Ayurveda's wisdom .
-
Investors
button

Read our recent and archived releases, quarterly results, annual reports and financial statements. Initiatives Investor Centre.
-
Newsroom
button

Welcome to Dabur Media Centre. In this section, you’ll find our latest Press Releases arranged in a chronological order. The Press Releases have been further
-
Ayurveda & you
button

Our curated Collection of Ayurvedic knowledge for you. We at Dabur are working towards helping people lead a healthy and balanced life.
-
Sustainability
button
Dabur has been engaged in community development activities since 1994 and is committed to making a positive contribution to the communities where we source, live, work and sell our products.
-
Join Us
button

At Dabur, we are very passionate about winning and this has been engrained in DNA of the organization.
-
Support
button
- Home > Ayurveda & you > Ayurveda & Science > Ayurvedic & Medicinal Plants
Ayurveda and Science
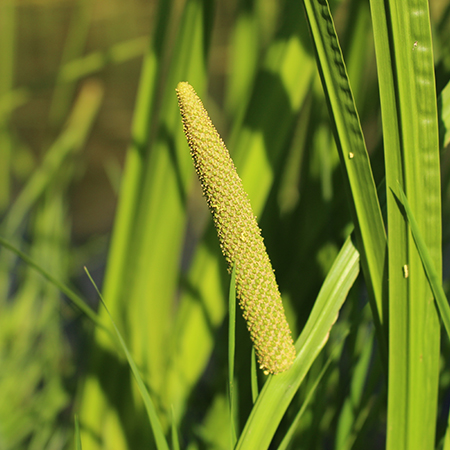
Ketaki/केतकी/Costus peciosus/Crepe Ginger/Kemukha
AYURVEDIC & MEDICINAL PLANTS
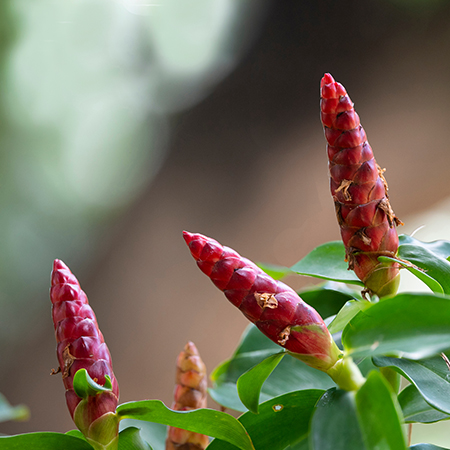

Costus Speciosus Medicinal Uses
Kemukha is primarily used by Ayurveda in the treatment of disturbances in lipid metabolism like obesity, hyperlipidaemia. It is also considered useful in the management of diabetes. It is thought to cause contraction in the uterine muscles. Therefore, has also been used to correct irregular menstruation and during parturition.
Chemical Composition
Tubers has a large amount of starch. Diosgenin and tigogenin have been isolated from the rhizome.
Balances kapha and pitta.
Read more about various ailments, it's causes, symptoms, ayurvedic treatments, etc.
Know the story behind other medicinal Ayurvedic ingredients

Mandukaparni

Palasha
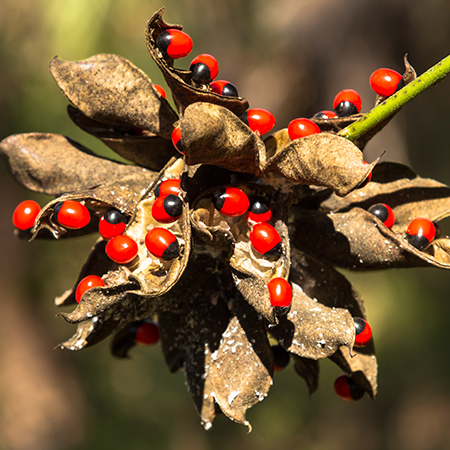

Ratti
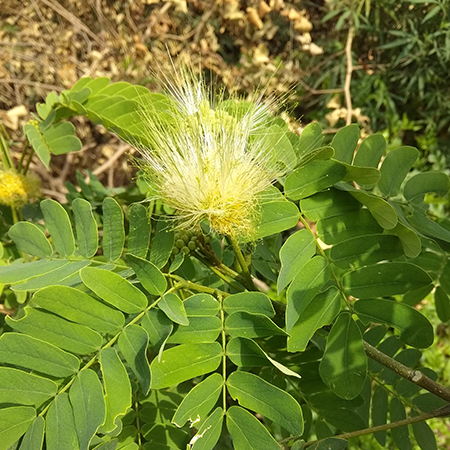

Shirish Plant
A deciduous erect spreading tree commonly growing at road side throughout India from the plains upto 900 m in Himalaya. Bark of the tree is used for various ailments in Ayurveda.





